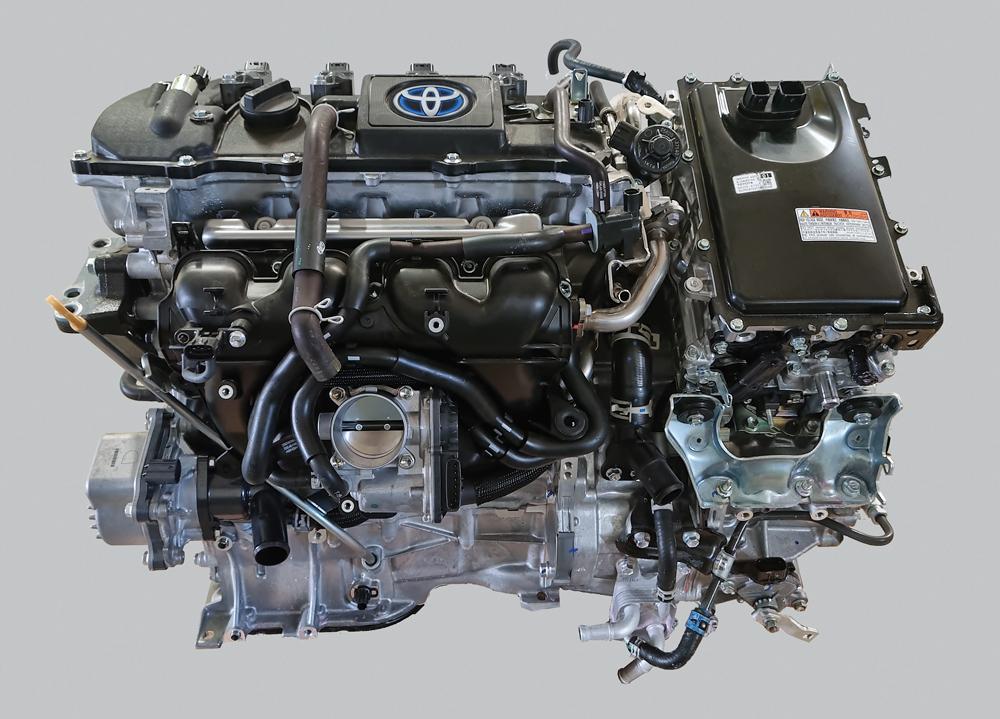






Toyota is one of the main manufacturers to invest considerable resources in the modern development of hybrid propulsion systems, as well as the first to market a hybrid production car, the Prius, at the end of 1997. Since that model it acquired a long and consolidated technological tradition through the development of various types of hybrid systems. The ZR series, introduced in 2007 and then subject to continuous updates, consists of various 4-cylinder models with different power outputs. The latest versions of these engines constitute the thermal part of hybrid systems characterized by a high level of efficiency, reaching up to 40% in optimal operating conditions. These performances, at the top of their category, are obtained thanks to various advanced features both in the internal combustion engine and in the electrical machine. Standing out among these are the valve timing control system, which allows the engine to operate according to the Miller-Atkinson cycle, and the Power-Split CVT transmission with continuously variable speed ratio. This combines the advantages of the more traditional series-hybrid and parallel-hybrid systems, eliminating their respective disadvantages: the power-split unit, whose fundamental element is an epicyclic gear train, allows the decoupling of the internal combustion engine from the road load as in the hybrid-series system, as well as, the simultaneous use of the engine together with all electric motors of the powertrain as in the parallel-hybrid arrangement.
Click here to listen to the audioguide on izi.TRAVEL
Toyota Prius 1.8 Hybrid
Toyota Corolla 1.8 Hybrid
Lexus CT
Kind donation of Toyota Italia.